
Why wood?

Certification
Certified Forests

Sustainability
Renewable product

Present/Future
Carbon positive
At Carmo Wood, we work with a wide range of wood products, from furniture to building materials and even residential construction. In all of them, we are committed to the quality and sustainability of our solutions.
A single tree can give rise to several different products through a circular production process. In our manufacturing method, we guarantee full utilisation of the wood.
Choosing wood for your projects should be an informed and conscious decision. On this page, we provide all the relevant information about this material and its many advantages.
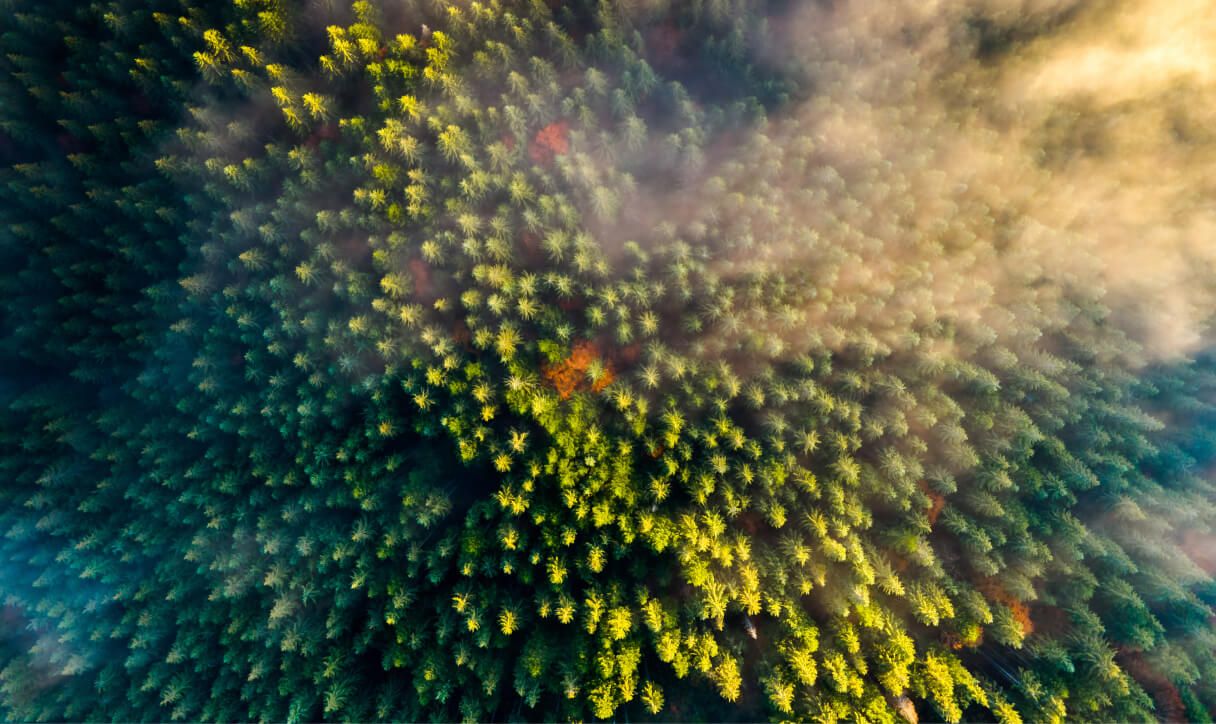

In a world increasingly concerned with sustainability and environmental impact, wood stands out from other solutions and materials.
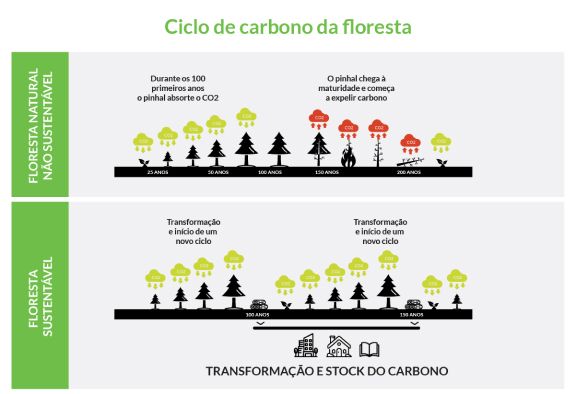
A sustainably managed forest is able to absorb carbon from the atmosphere and store it in each tree. This has a direct impact on reducing CO₂ levels in the environment and, as a consequence, mitigating climate change.
It also has features that make it easier to transport and use, increase thermal comfort and reduce waste production. All these issues are extremely important for the environment.
As well as being a natural material, wood is a sustainable choice for your projects. But it has several other advantages, both aesthetically and functionally:

Whether it's the first huts built by ancient civilisations or complex modern engineering structures made of wood, this building material has endured through time. Some ancient wooden structures that still stand today prove its durability and resistance.
The way in which this raw material connects us with the natural environment is one of the reasons why it remains so popular in contemporary design. Wood can provide a sense of calm and closeness to nature, even in urban environments.
That's why wood is more than just a building material. It is a bridge between the past and the future, between nature and man, between tradition and innovation. By choosing wood for your projects, you're not just opting for a material, but also for a heritage of value, sustainability and beauty.

Due to its characteristics, wood has enormous potential for construction. It represents an alternative to the usual materials, such as concrete or metal, with advantages for both the end customer and the planet.

- It is a renewable resource
Trees are replanted to replace those that have been harvested. Unlike other non-renewable materials such as concrete or steel, wood contributes to the conservation of forests.
- Retains carbon dioxide
Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it. In other words, wood is a way of reducing carbon emissions. In the case of treated wood, the carbon is stored for longer due to its durability.
- It has high structural strength
Wood is the material with the best weight-to-strength ratio, allowing for lightweight structures with high structural capacity.



To ensure its durability, wood must undergo a specific treatment. This treatment involves the application of chemical substances that protect it from fungi, insects and deterioration.
All the substances applied comply with the legislation applicable to biocides and do not harm people, animals or plants.
In order to define the treatment class, you need to realise what you are going to use the wood for. Different applications require different types of treatment, due to the humidity conditions to which it is subjected.
| Risk Class 1 | Risk Class 2 | Risk Class 3 | Risk Class 4 |
| Sheltered wood, protected from the weather and with a moisture content of less than 20 per cent. | Wood exposed occasionally to high humidity (under roofs or sheltered from rain) | Wood placed outdoors, frequently exposed to high humidity. Without contact with the ground. | Wood placed outdoors and in direct contact with the ground. |
| Examples: sheltered interior carpentry, such as floors, interior stairs and doors. | Examples: Interior beams, interior roof structures or roofs. | Examples: Exterior woodwork subject to rain (such as panelling and window frames), porches or roofs. | Examples: Decks, fences, walkways, wood in contact with the ground or moisture sources. |
| Class 1 low pressure autoclave treatment | Class 2 low pressure autoclave treatment | Vacuum and pressure in a Class 3 autoclave | Vacuum and pressure in a Class 4 autoclave |
Wooden construction is associated with a number of preconceived ideas, particularly regarding its durability and safety. Clear up some of the biggest myths about wood with us.
Madeira, a solução inetligente
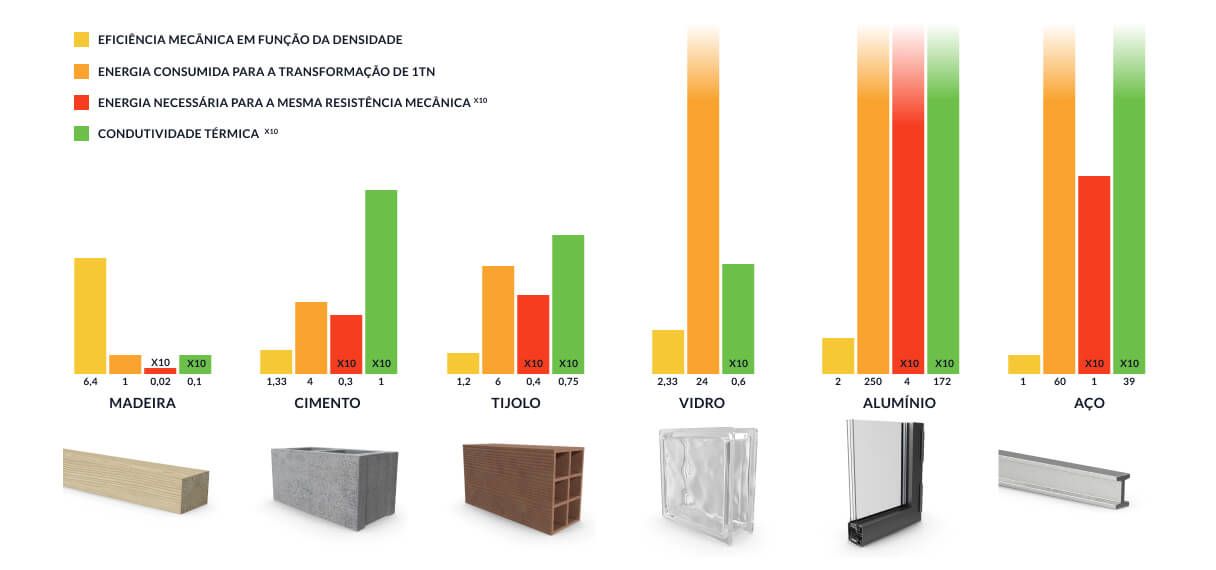
- Aço
- A madeira apresenta uma eficiência mecânica até 6,4 vezes superior ao aço, atribuída à sua menor densidade.
- Vidro
- Processar uma tonelada de madeira exige 24 vezes menos energia do que o vidro durante a sua produção.
- Alumínio
- Atingir uma resistência mecânica comparável consome 200 vezes menos energia com madeira do que com alumínio.
- Cimento
- A madeira apresenta uma condutividade térmica 10 vezes inferior à do cimento, proporcionando um isolamento superior.




| Wood | Plastic | Concrete | Metal | |
| Sustainability | Renewable resources | Finite and polluting resources | Significant CO₂ emissions | Intensive mining, environmental impact |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable | Not biodegradable, needs to be melted down | Not biodegradable, slow decomposition | Not biodegradable, may corrode |
| Durability | High durability | Around 10 years | Decades or centuries | High durability, corrosion resistant |
| Aesthetic | Natural and warm | Artificial and uncomfortable | Industrial, can be attractive | Bright and modern |
| Thermal and acoustic insulation | Good thermal and acoustic insulation | Low thermal and acoustic insulation | Good thermal insulation, poor acoustic insulation | Low insulation capacity |
| Waste Reduction | Less waste | Contributes to environmental pollution | Generates waste and CO₂ | Can generate significant waste |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight | Heavy | Heavier than wood or plastic |
| Transport and installation | Easy transport and work | Easy transport | Expensive and difficult transport | Difficult transport and installation |
| Cost | Competitive | Cheap and accessible | Expensive, high investment | High price |
| Energy efficiency | Lower energy consumption | High energy consumption | High energy consumption, emits CO₂ | High energy consumption |